

Major nerve pathways are seen as white striped patterns radiating from the optic disk. Veins are darker and slightly wider than corresponding arteries. The optic disk has some pigmentation at the perimeter of the lateral side, which is considered non-pathological. In this work fundus image of the retina is used. The gaze is into the camera, so the macula is in the center of the image, and the optic disk is located towards the nose (right in image). The segmentation of exudates is essential in differentiating the normal eye from the DR affected eye. The left image (right eye) shows lighter areas close to larger vessels, which is regarded as a normal finding in younger people. It is seen from front so that left in each image is to the person's right. The orange appearance of the normal fundus is due to complexes of vitamin A as 11-cis-retinal with opsin proteins in the retina (i.e., rhodopsin).
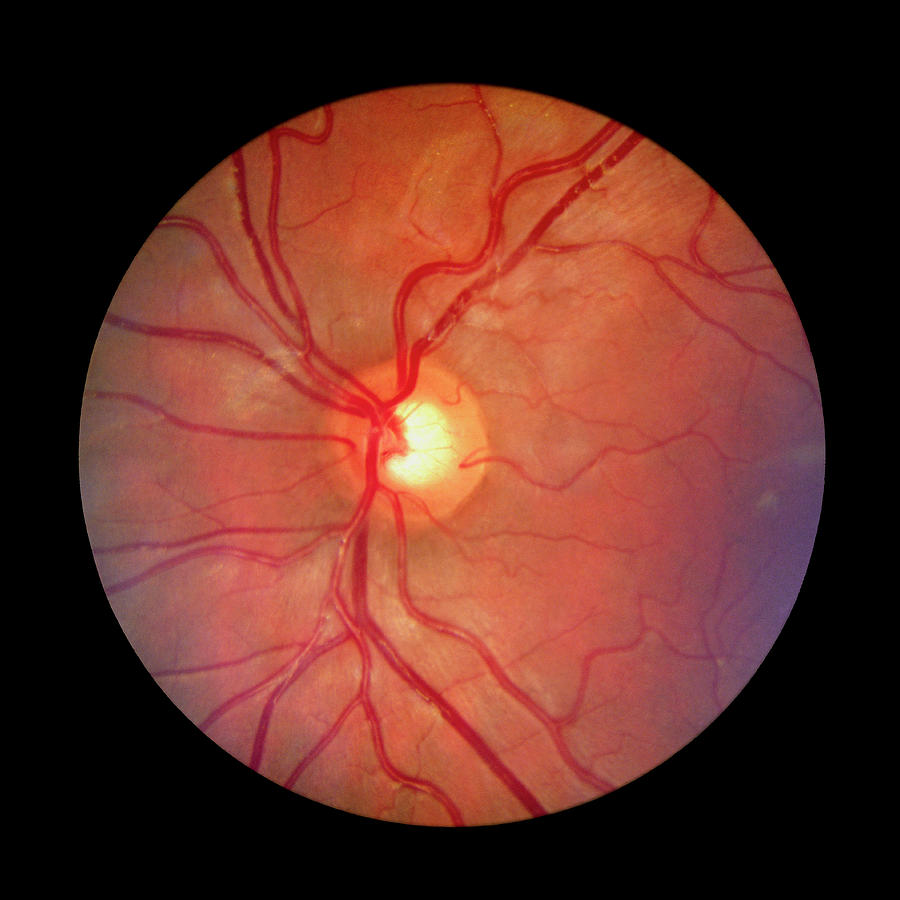
English: Fundus photograph of the right eye, showing a fundus with no sign of disease or pathology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
